What are the contents of pre-service training for employees of motor motor rotor duplex tester?
Motor motor rotor duplex tester employee pre-training content:
First, the basic knowledge of the equipment
l Introduction to the principle of work
Explain in detail how the tester can test the motor motor rotor, including the collection of rotor related data through various sensors (such as displacement sensors, speed sensors, pressure sensors, etc.), such as dimensional accuracy, rotational speed, balance, shaft withstand force and other parameters.
Explain the processing flow of the test data, such as how the data is transmitted to the control system, and how the control system analyzes and judges the data according to the preset criteria to determine whether the rotor is qualified.
Demonstrate the mechanical structure inside the testing machine and the principle of the electrical system working together in the form of schematic diagram or animation to help employees understand the overall operation mechanism of the equipment.
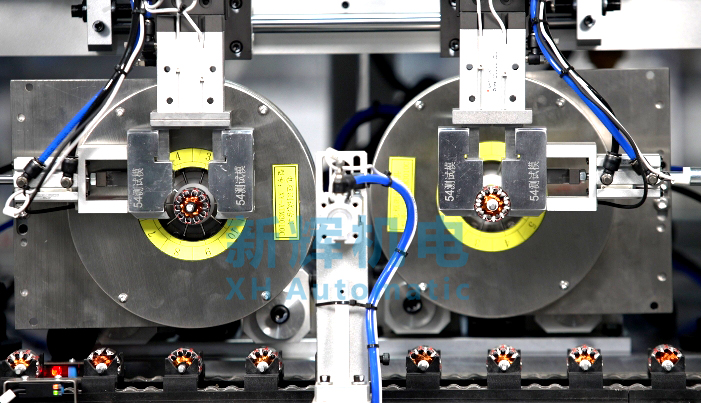
l Composition of equipment structure
Lead employees to recognize the main mechanical components of the tester, such as the test fixture, transmission mechanism (belt, chain, gears, etc.), worktable, positioning device, etc., and explain their functions and interconnections. For example, introduce how the test fixture precisely fixes the motor rotor to ensure the rotor's position is stable during the test; explain how the transmission mechanism realizes the conversion between different working stations and provides the necessary movement conditions for the test.
Explain the composition of the electrical system, including the location and role of electrical components such as power supply modules, controllers (e.g., PLCs, industrial controllers, etc.), sensors, relays, contactors, signal amplifiers, and so on. For example, explain how the power supply module provides a stable power supply for the whole equipment, and how the PLC controls the action sequence and logical relationship of each electrical component.
Second, equipment operation skills training
l Operation panel and software interface familiarization
Introduce to the staff the functions and operation methods of the keys, knobs and indicators on the operation panel of the tester, such as the start button, stop button, reset button, parameter adjustment knob, etc., as well as the status of the equipment represented by different indicators (such as running, fault, standby, etc.).
Train employees to be familiar with the software interface used by the tester, including how to log in the software, how to set up the test items and parameters (such as selecting the test type, inputting the rotor specification information, setting the test standard value, etc.), how to start and stop the test program, and how to view and analyze the test data and reports.
Practical operation demonstration, so that employees personally operate the operating panel and software interface, familiar with the operation process and the use of various functions, the trainer on the sidelines in a timely manner to correct the wrong operation.
l Test operation process standardization
In accordance with the standard operating procedures, we demonstrate in detail the entire operation process from placing the motor rotor on the test fixture to completing the test and removing the rotor. Including how to correctly install the rotor into the fixture to ensure good contact between the rotor and the fixture and accurate positioning; how to select the appropriate test program and parameters in the software according to the type and specifications of the rotor; how to start the test, how to monitor the operating status of the equipment and changes in the test data during the test process; how to view the test results report after the completion of the test to determine whether the rotor is qualified, as well as how to correctly remove the rotor. After the test is completed, how to check the test result report and determine whether the rotor is qualified or not, and how to correctly remove the rotor.
Allow employees to repeat the actual operation practice, in the practice process, the trainer strictly supervise, to ensure that the operation of the staff in line with the specifications, to be able to skillfully and accurately complete the test operation process, and develop good operating habits, such as checking the equipment before the operation, the operation process to maintain focus and caution, the operation is completed in a timely manner to clean up the work area, and so on.
Third, equipment maintenance and maintenance knowledge
l Daily maintenance points
Train employees in the daily use of equipment before and after the use of daily maintenance work. Before use, check whether there is any damage to the appearance of the equipment, clean the test fixture and the surface of the workbench, check whether the sensor probe is clean and free from foreign objects, check whether the electrical connections are loose or broken, etc.; after use, clean up the dust and sundries on the equipment, turn off the power supply of the equipment and the gas source (if any), and organize the test tools and related information.
Teach employees how to carry out daily inspection of the equipment, such as checking whether the clamping force of the test fixture is normal, whether the transmission mechanism runs smoothly (with or without abnormal noise, jamming, etc.), and whether the sensor has abnormal signal output, etc., and require employees to record the daily maintenance and inspection, so as to discover potential problems of the equipment and deal with them in time.
l Regular maintenance items and methods
Introduce the regular maintenance cycle of the tester (such as weekly, monthly, quarterly, etc.) and the corresponding maintenance program. For example, the transmission mechanism needs to be cleaned and lubricated every week to check whether the tension of the belt or chain is appropriate, and whether the gears are worn, etc.; the electrical system needs to be inspected in its entirety every month, including the cleaning of the circuit boards, checking whether the connection of electrical components is firm, and the accuracy of the test sensors, etc.; the mechanical precision of the tester needs to be calibrated every quarter, for example, by checking the positioning accuracy of the test fixtures, the table leveling, etc., and make adjustments as needed.
Train employees on how to carry out regular maintenance work, such as how to disassemble and install the components of the transmission mechanism for cleaning and maintenance, how to use professional tools (such as multimeters, oscilloscopes, etc.) to test and repair the electrical components, and how to use calibration tools (such as standard measuring blocks, calibrators, etc.) to calibrate the mechanical accuracy of the equipment. At the same time, emphasize the importance of regular maintenance work, only do a good job of regular maintenance to ensure the long-term stable operation of the equipment, reduce equipment failure and downtime.
Fourth, the operation specification and emergency measures
l Operation specification
Explain in detail to the staff the operation specification of the tester, including the inspection content before the start of the equipment, such as checking whether the protective device is intact, whether there are obstacles around the equipment, whether the power supply and gas source (if any) is normally connected, etc.; Precautions to be taken during the operation of the equipment, such as forbidding to open the protective door during the operation of the equipment, not touching the moving mechanical parts, preventing the hair and clothes from being involved in the transmission mechanism, etc.; Equipment Requirements for operation after the equipment stops, such as stopping the test program before turning off the power supply and gas source, and cleaning up the workplace.
Train employees in the proper use of personal protective equipment, such as protective glasses and gloves, and require them to wear them strictly during work. For example, protective gloves must be worn during test operations to prevent hands from being caught by fixtures or scratched by the rotor; protective glasses may be required when cleaning equipment to prevent dust and debris from splashing into the eyes.
l Emergency Measures
Teach employees how to deal with emergencies that may occur during equipment operation, such as sudden power outages, abnormal movements due to equipment failure, and fires. For example, in the event of a sudden power failure, employees should know how to turn off the power switch and gas switch (if any) of the equipment to prevent the equipment from automatically starting up after an incoming call and causing danger; when there is an abnormal movement of the equipment, such as the fixture is out of control, employees should immediately press the emergency stop button and stay away from the equipment and wait for professional maintenance personnel to deal with it; in the event of a fire, employees should be familiar with the use of the extinguishers and the location of evacuation routes, and be able to quickly take action to extinguish the fire and the evacuation routes. location, and be able to quickly take fire extinguishing and evacuation measures.
Conduct emergency drills to simulate various emergencies and let the employees actually operate the emergency treatment process, so as to improve their emergency response ability and self-protection awareness. At the same time, employees are required to remain calm when encountering emergencies and deal with them in an orderly manner in accordance with the trained emergency handling measures, without panicking and acting blindly.
V. Quality control and testing standards
l Test quality standards
Explain to the staff the various standards and requirements of test quality, including the qualified range of various test parameters of different types of motor rotors (such as dimensional tolerance, speed error, balance index, etc.), the accuracy of test data and repeatability requirements. For example, it is stipulated that the diameter size tolerance of the motor rotor is within ±0.05mm, and the speed error shall not exceed ±5%, etc. Samples of qualified and unqualified test results are displayed to let the employees intuitively understand the difference in test quality, which facilitates the employees to carry out quality control in the actual operation.
Teach employees how to use the tester software and related tools to detect and monitor the test quality, such as how to view the statistical analysis results of the test data, how to compare the difference between the test data and the standard value, how to determine whether the repeatability of the test data meets the requirements, etc., and require employees to carry out regular quality inspections during the testing process, and make timely adjustments when problems are found.
l Quality problem analysis and solution
Train employees how to analyze the quality problems in the testing process, such as abnormal test data may be caused by sensor failure, loose test fixture, wrong parameter settings, etc.; unqualified rotor test may be due to manufacturing defects in the rotor itself, the precision of the tester decreases, and so on. By analyzing quality problems, employees can find the root cause of the problem and take appropriate measures to solve it.
For example, when abnormal test data are found, employees should first check the connection and working status of the sensor, then check whether the test fixture is firm, and then check whether the parameter settings are correct; when the rotor test is unqualified, the employees should comprehensively consider factors such as the manufacturing process of the rotor and the recent maintenance of the testing machine, and if necessary, communicate and collaborate with relevant departments (such as the production department and the maintenance department, etc.) to jointly solve the quality problems.
※ If there is any other help, please contact the technical specialist of Xinhui Electromechanical Equipment Co., Ltd. through the page chat tool for assistance.







