Motor motor rotor manual six-station double flying fork winding machine staff pre-employment training content?
Motor motor rotor manual six-station double flying fork winding machine staff pre-training content should cover the operation of equipment, quality control, maintenance and troubleshooting and other aspects, as follows:
First, the equipment overview and principle
1, the structure of the introduction
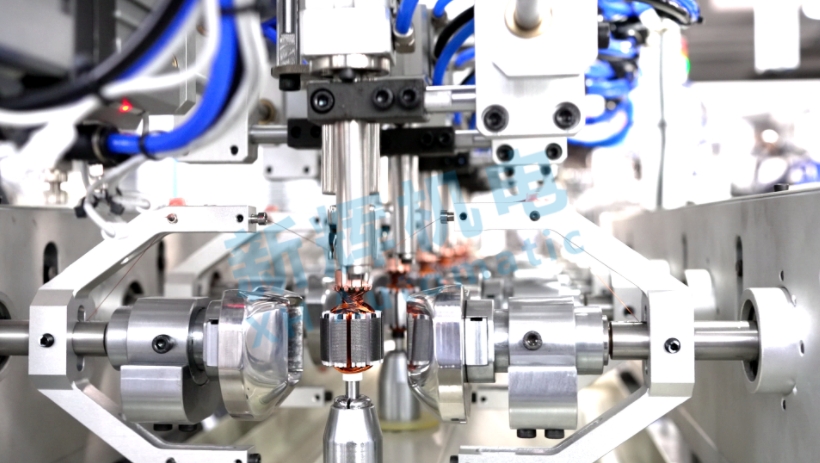
l Detailed explanation of the overall structure of the winding machine, including the specific functions and layout of the six stations, such as winding station, rotor feeding station, unloading station, etc..
l Introduce the structure and working mode of the double flying fork, how the flying fork carries out the winding action under the motor drive, and the synergistic relationship between the flying fork and other parts (such as fixture, guide rail, etc.).
l Demonstrate the mechanical transmission system of the equipment, such as belts, chains, gears and other transmission components of the location and role, so that employees understand how the power is transmitted to the various moving parts.
l Explain the main components of the electrical control system, such as controllers, drives, sensors, motors, etc. in the position and function of the equipment, so that employees have a preliminary understanding of the electrical structure of the equipment.
2、Working principle explanation
l Explain the winding principle of the winding machine, including how to accurately wind the wire according to the set number of turns, wire diameter and other parameters, and how to cooperate with the rotary and translational movements of the flying fork to realize the winding of the wire on the rotor.
l Explain the automation control process of the equipment, such as how the rotor is automatically transferred between the stations, how the sensors detect the rotor position and status and feedback signals to the controller to trigger the corresponding action, and how the controller coordinates the work of various components according to the preset program.
Second, equipment operation specification
1、Power on and off process
l Train the preparatory work before starting the machine, such as checking whether there is any damage to the appearance of the equipment, whether the cleaning work is in place, whether the components are in normal position (such as whether the flying fork is in place, whether the clamps are loosened, etc.).
l Detailed demonstration of power-on procedures, including the order of power on, start the controller and drive operation, equipment initialization process of attention (such as observing whether the lights are normally lit, whether there is no abnormal alarm sound, etc.).
l Explain the shutdown process, such as how to stop the winding action after the completion of the winding task, how to shut down the motor and drive, the controller shutdown operation and cut off the power supply in order to emphasize the importance of shutting down the equipment after the necessary organization (such as cleaning up the work area, put away the tools, etc.).
2、Parameter setting method
l Teach the staff how to enter the parameter setting interface of the equipment, different brands and models of winding machines may have different operating methods, need to let the staff master.
l Explain in detail the meaning and setting range of winding parameters, such as the number of turns setting, to let employees understand that the wrong number of turns will lead to the rotor winding does not meet the requirements; wire diameter setting, which affects the tightness of the winding and tension control; winding speed setting, need to take into account the material of the rotor, the type of wire and the mechanical properties of the equipment and other factors to be reasonably determined, too high or too low a speed will affect the quality of the winding and the life of the equipment.
l Train the staff how to accurately set the parameters according to the actual production tasks, and save and call the parameters of the operation, while emphasizing the need to change the parameters of the trial run to ensure the correctness of the parameter settings.
3、Manual operation skills
l Teach employees how to carry out manual loading operations, including how to correctly place the rotor in the designated station on the fixture, how to ensure that the rotor is installed firmly and accurately positioned, as well as how to avoid collision with the equipment components in the process of placement.
l Demonstrate manual winding operation, such as how to manually control the movement of the flying fork for winding when the automatic winding function fails or when special winding tasks are required, including the techniques of starting, stopping, forward and reverse rotation of the flying fork and the control of the moving speed.
l Training manual unloading operation, explaining how to remove the wound rotor from the fixture, and how to place it in the designated collection area after removing it, to avoid damage to the already wound bobbins.
4、Automatic operation and monitoring
l Familiarize the staff with the starting conditions and operation methods of the automatic operation of the equipment, such as how to start the automatic winding program of the equipment after setting up the parameters and confirming the readiness of each component, so that the rotor can complete a series of automatic operations such as loading, winding, and unloading in each station in turn.
l Train the staff in the automatic operation of the equipment how to monitor the process, including observation of the operating status of the equipment (such as flying fork movement is smooth, whether the transition of the workstation is normal, etc.), view the real-time data on the controller display (such as the number of turns counting, winding speed, tension value, etc.) as well as pay attention to listen to the equipment running with or without abnormal sound, if found abnormal how to stop in time to deal with.
Third, the protection of knowledge and attention
1、Introduction of protection devices
l Introduce the various protective devices on the winding machine to the staff, such as the position and function of the emergency brake button, and how to quickly press the emergency brake button to stop the operation of the equipment when encountering a sudden dangerous situation (such as the body parts of the personnel are about to be rolled into the equipment, serious equipment failure, etc.).
l Explain the role of the protective door or guardrail, in the process of equipment operation, employees are not allowed to open the protective door or cross the guardrail, in order to avoid danger, only in the case of stopping the equipment can be related to the operation (such as equipment maintenance, adjustment, etc.).
l Introduce the principle and function of photoelectric sensors and other protection and detection devices, these devices are used to detect whether the personnel or foreign objects into the hazardous area of the equipment, once the abnormalities detected, the equipment will be automatically triggered to shut down or alarm, so that employees understand the scope of its work and the trigger conditions, to avoid misuse leading to its failure.
2、Emphasize the operating procedures
l Emphasize the need to wear personal protective equipment before operating the equipment, such as work clothes, work shoes, protective glasses, etc., to prevent accidental injuries during operation (e.g., scratched eyes by the line, touched body by the equipment parts, etc.).
l It is strictly prohibited to carry out cleaning, debugging, maintenance and other operations during the operation of the equipment. If such operations are required, the machine must be shut down and the power supply must be cut off first to ensure that the equipment is in a state of complete cessation and free from any hidden dangers, so as to prevent injuries or damage to the equipment due to misoperation.
l Inform employees not to arbitrarily change the settings and parameters of the equipment, such as the locking time of the protective door, the sensitivity of the emergency brake button, etc. These settings have been professionally debugged and verified, and arbitrary changes may reduce the protective performance of the equipment.
l Train the staff to maintain a good working environment around the equipment, not to pile up debris, to avoid affecting the normal operation of the equipment, and at the same time pay attention to the ventilation and heat dissipation when the equipment is running, to prevent overheating caused by fire and other accidents.
3、Training on emergency measures
l Employees in the event of accidents (such as injuries, equipment fire, etc.) emergency measures, such as injuries in the personnel, should immediately stop and call for rescue personnel, the injured person to carry out simple first aid treatment (such as bleeding, bandaging, etc.); in the event of a fire in the equipment, you should quickly use the nearby fire extinguishers to extinguish the fire, and immediately report to the higher-ups and the relevant departments.
l Conduct emergency shutdown and evacuation drills, so that employees are familiar with how to quickly press the emergency brake button to stop the operation of the equipment in the event of an emergency, as well as how to quickly evacuate in accordance with the pre-determined evacuation routes, to improve the staff's ability to respond to emergencies and self-protection awareness.
Fourth, quality control points
1、Winding quality standard explanation
l Detailed introduction to the winding quality standards and requirements, such as wire winding on the rotor should be tight, uniform, no loose, cross, overlap and other phenomena, the gap between the wire should be in accordance with the specified tolerance range.
l Explain the accuracy requirements of the number of turns, the number of winding turns must be in strict accordance with the design requirements, the error must not exceed a certain range, otherwise it will affect the performance and parameters of the motor.
l Emphasize the tension control requirements of the line, too much tension may lead to line breakage or rotor deformation, too little tension will make the winding not close, affecting the insulation performance and electrical parameters of the motor, so that employees understand how to control and adjust the tension through the tension adjustment device of the equipment.
2、Quality inspection methods and tools
l Train employees to use commonly used quality inspection tools, such as turns counter, wire diameter measuring instrument, tensiometer, etc., so that employees are proficient in the operation of these tools and reading skills, and be able to accurately measure the number of turns of the winding, wire diameter and tension value.
l Teach the staff to carry out the inspection of the appearance of the winding quality, such as through visual inspection of the winding of the wire, whether there is damage or burrs and other defects, and how to use the feel to determine the tightness of the winding and the tension is uniform.
l Let the staff understand the method and frequency of sampling inspection, in the mass production process, how to wind the rotor in accordance with a certain proportion of sampling inspection to ensure that the quality of the entire batch of products in line with the requirements of the product, if found to be substandard how to identify, isolate and deal with.
3、Prevention of quality problems and corrective measures
l Analyze the causes of common quality problems, such as improper parameter settings leading to winding quality problems (wrong number of turns, abnormal tension, etc.), equipment failure (such as unstable fork movement, loose fixtures, etc.) leading to winding defects, quality problems caused by human error (such as inaccurate position of the rotor when loading, manual winding operation is not standardized, etc.), so that employees can understand the reasons for these causes so as to prevent the problem in the course of operation. l Train the employees to know the causes of quality problems when they find quality problems.
l Train the staff how to take corrective measures in time when quality problems are found, such as stopping the machine immediately to check whether the parameter settings are correct, whether the equipment components are normal, and evaluate and deal with the rotors with quality problems (such as rework, scrap, etc.), and at the same time report the quality problems to the supervisor in time so as to make adjustments and improvements to the production process.
V. Maintenance knowledge
1、Daily maintenance content and methods
l Train employees to carry out daily cleaning work, such as how to use a clean soft cloth to wipe the dust, oil and debris on the surface of the equipment after each use of the equipment, especially on the flying forks, fixtures, guide rails and other key components of the cleaning should be careful and serious, to prevent the accumulation of dirt affecting the performance of the equipment.
l Teach employees how to carry out daily inspection and lubrication of mechanical parts, such as checking whether the tension of belts and chains is appropriate, and how to adjust them if they are slack; checking whether there is wear and tear of gears, missing teeth, etc.; and how to add the right amount of lubricant or grease on a regular basis on guide rails, sliders, bearings, and other moving parts, in order to minimize friction and wear, and to ensure that the parts are moving smoothly.
l Let employees understand the main points of daily electrical system inspection, such as checking whether the power line and signal line are firmly connected, and whether there is any sign of looseness, oxidation or breakage; observing whether the indicator light of the equipment is normally on, and whether there is any abnormal flashing or extinguishing phenomenon; and simply testing whether the motor's starting and stopping functions are normal before starting the machine.
2、Regular maintenance program and process
l Introduction of regular maintenance intervals and project content, such as every period of time (such as a week, a month or a quarter, according to the frequency of use of equipment and manufacturers to determine the recommendations) for a full inspection and maintenance of equipment.
l Detailed explanation of regular maintenance items, such as deep cleaning and disassembly of mechanical components to check the wear and tear of internal parts such as the rotor shaft and bearings of the flying fork, and replace the parts with serious wear and tear; carry out a full inspection of the electrical system, including cleaning the circuit board, checking the accuracy and installation position of sensors, and testing the insulation resistance of the motor; and carry out a data backup and updating check of the software system of the equipment. l Demonstrate the operation of regular maintenance.
l Demonstrate the operation process of regular maintenance, so that employees are clear about the sequence and operation points in the maintenance program, such as in the disassembly of mechanical components should be how to mark and record, in order to correctly assembled; in the cleaning circuit boards should be used to avoid damage to the circuit boards and other tools and cleaning agents.
3、Maintenance records and reporting requirements
l Train employees how to fill in the maintenance records, records should include maintenance time, project content, inspection results, replacement of parts and components information as well as the operator's signature, etc., in order to trace the maintenance history of the equipment and management.
l Let the staff understand the equipment found to have major faults or abnormalities in how to write maintenance reports in a timely manner, the report should describe in detail the failure phenomenon, the possible causes of the analysis and the proposed maintenance measures to be taken to the supervisor and the equipment management department to report, so as to arrange for the maintenance of professional personnel and processing.
Sixth, the basis of fault handling
1、Common fault phenomenon identification
l Introduce the common fault phenomena of the winding machine, such as the motor does not rotate, abnormal flying fork movement, inaccurate winding turns, uncontrolled tension, equipment alarms, etc., so that employees can quickly and accurately identify these fault phenomena, and understand their possible impact on the quality of the winding and the operation of the equipment.
l Through pictures, videos or actual cases to show a variety of fault phenomena, so that employees have a more intuitive understanding of the fault, such as showing the motor does not rotate when the performance of the equipment (motor no sound, flying fork does not move, etc.), flying fork movement abnormal trajectory deviation or stuck phenomenon, etc., to help employees in the actual operation of the fault in a timely manner.
2、Simple troubleshooting and handling methods
l Train employees to troubleshoot and deal with some simple faults, such as when the motor does not rotate due to the loose power cord, how to check the connection of the power cord and re-plug it so that it is firm; when the flying fork movement is stuck due to the debris in the guide rail of the flying fork, how to clean up the debris in the guide rail so as to make it return to smoothness; when the number of turns of the winding wire is inaccurate due to the error in parameter setting, how to re-enter the parameter setting interface to check and modify the parameters, etc. l Provide the ideas and methods to help staff find faults in time during the actual operation.
l Provide troubleshooting ideas and steps, such as starting with the appearance of the equipment to check whether there is obvious damage or abnormalities, and then check the electrical connection, mechanical transmission and other systems, gradually narrowing the scope of troubleshooting to determine the cause of the failure and then take appropriate measures to deal with, so that employees can master the basic skills of troubleshooting.
3、Fault report and assistance in maintenance process
l Teach employees how to write a fault report when they encounter a fault that cannot be handled by themselves, the report should include the time of the fault, a description of the fault phenomenon, the investigation and treatment measures that have been taken, as well as the impact of the fault on the production and other information, so that the maintenance staff can quickly understand the fault situation and prepare the appropriate maintenance tools and accessories. l Familiarize employees with the submission of fault reports, so as to enable them to grasp the basic troubleshooting skills and assist in maintenance.
l Let the staff familiarize with the failure report submission channels and assist in the maintenance process, such as to whom to report the failure (such as workshop supervisor, equipment maintenance department, etc.), maintenance personnel to arrive at the scene of the cooperative work (such as providing information on the operation of the equipment, to assist in fault reproduction, etc.) and in the maintenance process how to learn from the maintenance staff's handling methods and experience, to improve their own troubleshooting capabilities.







