Motor motor rotor duplex tester how to carry out maintenance?
Motor motor rotor duplex tester maintenance guide:
I. Daily maintenance
l Cleaning
Body cleaning: After each use, wipe the tester body with a clean soft cloth to remove dust, oil and other impurities on the surface. Focus on cleaning the test fixtures, sensor probes, motor housing and other parts, because these places are easily contaminated with dust and oil, affecting the test accuracy and equipment performance.
Internal Cleaning (Periodic): At regular intervals (e.g., weekly or biweekly), open the casing of the tester and use a small vacuum cleaner or a can of compressed air to clean the dust inside. Pay particular attention to cleaning the dust inside the circuit board and electrical control cabinet to prevent excessive accumulation of dust causing short circuit or poor heat dissipation.
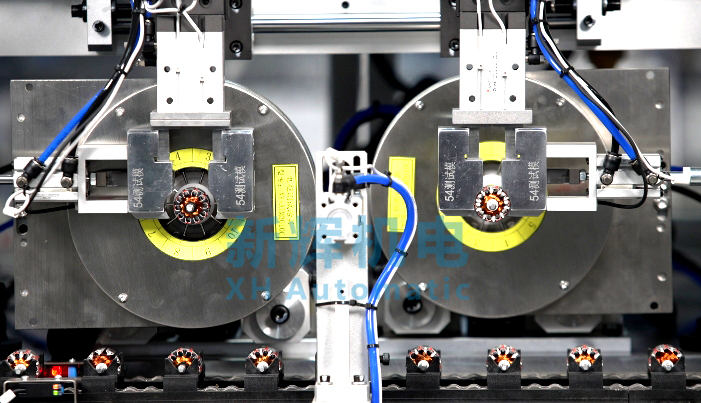
l Check the mechanical components
Fixture inspection: Check whether the clamping force of the fixture is normal, and whether the collet and locating pin are worn out. Test the accuracy of the fixture by clamping standard parts to ensure that it can accurately fix the motor rotor. If the collet is found to be worn, it should be replaced in time; if the positioning pin is worn and affects the positioning accuracy, it also needs to be replaced.
Transmission mechanism inspection: Check the tension and wear of transmission parts such as belts, chains and gears. For the belt and chain, check whether there is slack, if necessary, in accordance with the requirements of the equipment manual for adjustment; observe whether the gear tooth surface wear, lack of teeth, etc., wear serious gear should be replaced in a timely manner. At the same time, check the lubrication of the transmission parts to ensure that there is enough lubricant.
Workbench inspection: check whether the surface of the workbench is flat, with or without scratches or deformation. If the surface of the working table is not flat, it may affect the placement of the motor rotor and test precision, at this time the working table needs to be repaired or replaced. Check whether the fixing screws of the worktable are loose, if loose, they should be tightened in time.
microsoft screenshot_20241206083511.png
l Check the electrical system
Connection line check: Check whether the wires inside and outside the tester are firmly connected and whether the plugs and sockets are in good contact. Check whether the wires are broken, aging, etc. If found, the wires should be replaced in time. Pay special attention to check the sensor signal line, motor power line and other key lines.
Electrical component inspection: Observe the appearance of the electrical components (such as relays, contactors, switches, etc.) to see if there are any abnormalities such as burnt or deformed. Use a multimeter and other tools to check the working status of the components, such as checking whether the coil resistance of the relay is normal, whether the contacts of the contactor are good and so on. For the faulty electrical components, they should be replaced in time.
Sensor inspection: Check whether the probe of the sensor is clean and has no damage. For example, if the probe of the displacement sensor is covered with oil or dust, it will affect the measurement accuracy and needs to be wiped clean with a clean cloth; check whether the probe of the temperature sensor has signs of looseness or damage. At the same time, check whether the signal output of the sensor is normal, which can be judged by connecting an oscilloscope or viewing the sensor data on the tester software.
II. Regular maintenance (monthly or quarterly)
l Mechanical components maintenance
Lubrication work: lubricate all mechanical parts that need lubrication all the time. According to the requirements of the equipment, select the appropriate lubricant (such as lubricating oil, grease), and use special lubrication tools to apply. Key lubrication parts include gears, screws and guide rails of the transmission mechanism, and movable joints of the fixture. Ensure that the lubricant is applied evenly and avoid too much or too little.
Accuracy calibration: Calibrate the mechanical accuracy of the tester regularly. Use professional measuring tools (e.g. calipers, micrometers, levels, etc.) to calibrate the positioning accuracy of the fixture, the level of the worktable, etc. If the accuracy is found to be out of the allowable range, the relevant components need to be adjusted or repaired. For example, restore the positioning accuracy by adjusting the positioning screws of the fixture and use shims to adjust the level of the table.
Tightening of mechanical parts: Check and tighten the connecting screws of all mechanical parts. Since the equipment generates vibrations during operation, which may cause the screws to loosen, they need to be inspected periodically. Particular attention should be paid to checking those screws that are subject to larger loads or vibration parts, such as motor mounting screws and fixture fixing screws.
l Electrical system maintenance
Maintenance of electrical control cabinet: Clean up the dust and debris in the electrical control cabinet to ensure good ventilation and heat dissipation. Check whether the wiring in the control cabinet is neat and orderly, and whether the marking is clear. For aging or damaged wires, they should be replaced and re-labeled. At the same time, check whether the grounding inside the control cabinet is good to prevent electric shock accidents.
Testing and maintenance of electrical components: Use professional electrical testing equipment (such as insulation resistance meter, voltage tester, etc.) to test electrical components. For example, measure the insulation resistance of transformers and check the voltage resistance of capacitors. Replace or repair components that have deteriorated in performance or show signs of failure in a timely manner. For core control equipment such as PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and industrial controllers, follow the equipment manufacturer's recommendations for maintenance, such as backing up programs and clearing caches.
Sensor Calibration: Calibrate sensors periodically to ensure measurement accuracy. Use standard calibration equipment (e.g., standard displacement block, standard resistance box, standard temperature source, etc.) for calibration according to the type of sensor and equipment requirements. During the calibration process, record the calibration data, compare the difference between the actual output of the sensor and the standard value, and if there is any deviation, adjust the parameters of the sensor or carry out maintenance.
III. Long-term maintenance (every year or every two years)
l Complete overhaul of mechanical parts
Dismantling and inspection of mechanical parts: Dismantle and inspect the main mechanical parts of the tester, including fixtures, transmission mechanism, working table, etc. Check the wear and tear inside the parts, such as the wear and tear of the bearings, the wear and tear of the silk rod, etc.. For serious wear parts, should be replaced. At the same time, check the lubrication inside the parts, clean the old grease and reapply the right amount of new grease.
Mechanical parts replacement and upgrading: according to the use of equipment and technological development, consider replacing some mechanical parts with declining performance. For example, replace an old belt drive with a more accurate screw drive, or upgrade an ordinary fixture to one with higher precision and clamping force. When replacing or upgrading components, make sure the new part is compatible with the rest of the machine and follow proper installation procedures.
Mechanical system performance test: After completing the overhaul, replacement or upgrading of mechanical components, conduct a full performance test of the tester's mechanical system. By simulating the actual test scenario, check the performance indexes of the equipment such as operation stability, accuracy retention and so on. If problems are found, timely adjustments and optimization are made to ensure that the equipment can meet the testing requirements.
l Electrical System Upgrade and Remodeling
Upgrade of electrical components: With the continuous progress of technology, consider upgrading the electrical components of the testing machine. For example, replace the sensor with better performance, more advanced PLC or industrial control machine. When upgrading electrical components, pay attention to the compatibility of components to ensure that the new components can be seamlessly integrated with the existing system. At the same time, conduct all tests on the upgraded electrical system, including function tests, communication tests, etc.
Optimization and transformation of the electrical system: according to the actual testing requirements and technological development, the electrical system of the tester is optimized and transformed. For example, increase the data acquisition and processing functions to realize the automated testing process; or redesign the electrical control cabinet to improve its electromagnetic compatibility. In the transformation process, follow the relevant electrical standards and specifications to ensure that the transformed electrical system is reliable.
Electrical system backup and recovery: Regularly back up the important data of the electrical system (e.g. PLC program, industrial control machine software configuration, test parameters, etc.). You can use external storage devices (e.g. USB flash disk, removable hard disk) or cloud storage service for backup. When the electrical system fails or needs to be recovered, the backup data can be used for recovery in time to reduce equipment downtime.
※ If you still can't solve the problem by the above ways and means, please contact the technical specialist of Xinhui Electromechanical Equipment Co.







